Comparison of Interferon-Gamma Release Assay Tests in Tuberculosis Detection
About Tuberculosis (TB)
TB is an infection triggered by a bacterium named Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Transmission of this illness occurs through droplet inhalation, or when someone inhales a small droplet of a sneeze or cough from an infected patient. This makes it important to use isolation precautions if someone has a confirmed TB case. The bacteria can cause a variety of symptoms but most commonly affects the lungs. It also can attack the kidneys, central nervous system and other organs since the bacterium can travel through the blood stream. Patient symptoms vary so greatly that for some the condition can be fatal, yet others show no symptoms. The most common symptoms are a cough that lasts weeks, persistent phlegm and chest pain. Other symptoms are fatigue, unexplained weight loss, lacking appetite, chills and fever. Those with a weakened immune system, as seen with HIV infection or diabetes mellitus, are the most at-risk for TB.
Latent TB Infections (LTBI)
Even if a patient does not show symptoms, the bacteria can lay dormant in the body. This is known as a separate but similar condition called Latent TB infection (LTBI). These individuals will usually show a positive TB test but will have a normal chest x-ray. LTBI patients are not contagious but the condition can resurface into an active TB infection if the patient’s immune system is comprised. It is important that LTBI patients still complete a full course of therapy.
Available Testing and Prevention
As with many illnesses, prevention is a great method in areas where this disease is very prevalent. The vaccine for TB is given to young children in countries with a high TB rate, such as Africa, South Asia and South America. The vaccine is not regularly used in the United States since the disease incidence rate is very low in this country. The lack of vaccination does create the need for testing and treatment when illness does occur. For those with confirmed TB, it is usually treated with a 6 month treatment plan of antibiotics.
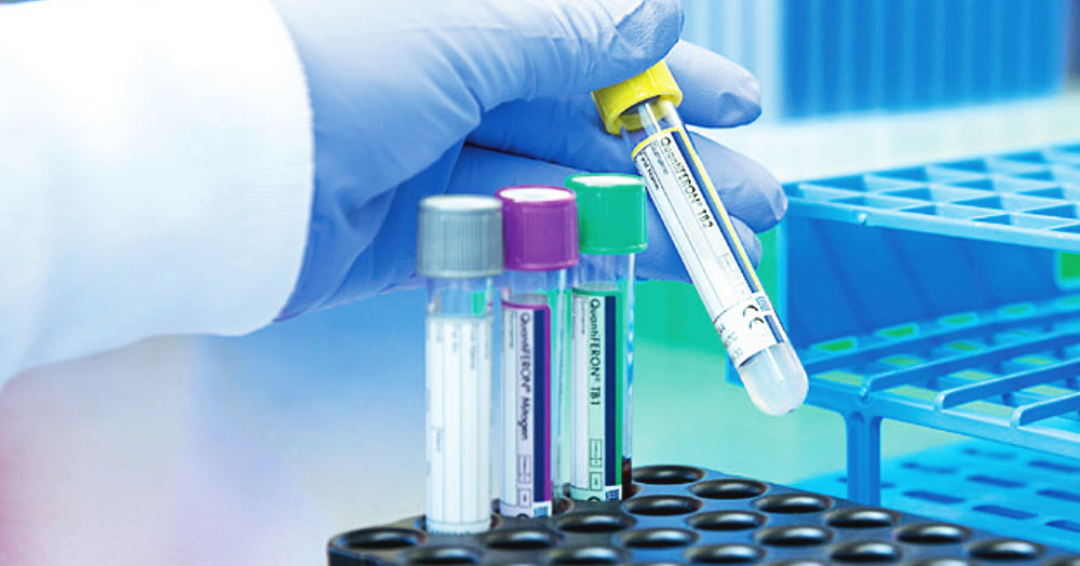
In the United States, there are two Interferon-Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) tests, approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA): TB Gold and T-SPOT TB Test. These are single visit, blood tests and must be administered by a medical professional then sent to a laboratory for analysis. This is in comparison to the traditional skin test, which requires two visits. These IGRA tests can be used by itself or as a second confirmation after a skin test. While IGRA are more accurate and more reliable than the traditional skin tests, they are also more expensive. This test stands out against traditional skin tests, due to its enhanced ability to diagnose LTBI. It is also the preferred type of test for those who have received the TB vaccine, Baccille Calmette-Guérin. With this test, a positive result supports that this bacterium is in your body and the diagnosis can be TB or LTBI. The next step would be to see a physician for a physical examination, chest x-ray and to discuss your exposure risk. A negative result means that it is unlikely that the TB infection is in your body. There is a third result, referred to as indeterminate, which means further exploration by medical professionals is necessary.
QuantiFERON TB Gold Plus
The QuantiFERON-TB Gold test measures the immune system response of T cell activation to a possible Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Particularly, these immune responsive T- cells become sensitized to the exposure of several high-specificity TB antigens. The QuantiFERON-TB Gold test uses a single mixture of these several antigens. The exposure to these causes the immune system to yield Interferon-? (IFN-?). This existence or absence of this molecule associates to a diagnosis of TB. Additionally, the magnitude of immune response can be determined through a QuantiFERON-TB Gold test, which gives a physician a broad view of the illness and can help in treatment. This test has demonstrated usefulness in younger patients (7-9 years old), as well as those with HIV co-morbidity. The QuantiFERON-TB Gold test is effective and efficient. This test boasts 97% specificity, although some studies have found poorer sensitivity with increasing age. Additionally, it has a 24 hour turnaround time, although that can be elongated due to laboratory and provider delay. A shortcoming for this test is that it needs a special syringe, which can disrupt test results and create the need for retests.
T-SPOT TB Test
T-SPOT TB test is also a single visit, blood test. This is the only blood test cleared by the FDA for patients as young as 2 years old. Enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) methodology is used by the T-SPOT TB test to similarly count the T cells that have been sensitized by TB infection, as described above. T-SPOT uses a larger number of cells than other blood tests, such as QuantiFERON-TB Gold, as it aims to lower inconsistency and enhances sensitivity for this infection. This method also uses separate mixtures of the high- specificity TB antigens. One study notes that T-SPOT test’s sensitivity was not affected by age or if the patient was immunosuppressed. This test uses standard phlebotomy equipment and does not see the same need for retest. The results can be concluded in 24 hours, typically most take 36-48 hours from sample acceptance.
Conclusion
Overall, TB is a serious condition that requires adequate and accurate testing. Both IGRA tests are better options than the traditional skin tests due to higher specificity and ability to identify LTBI. The choice on which test will be better for either you or your company will likely come down to cost.
Need TB Testing for your Employees or Candidates?
NMS Health has over 7,000 partnered locations throughout the U.S. that complete IGRA testing. NMS Health currently only offers the QuantFERON Gold Plus test.
In our intuitive platform Pod, our clients can order screenings, view live statuses and manage annual compliance all in one place. Our clients save an average of 60 minutes in administrative work per employee and reduce costs in the process!
Click here to Learn More and to get started today!
Resources:
https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/testing/tbtesttypes.htm
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/tuberculosis-tb/
https://www.quantiferon.com/us/products/quantiferon-tb-gold-plus-us/laboratory-resources/